Kinetic Study of α-cellulose Hydrocracking Using Ni and Pd Supported on Mordenite Catalysts
Triyono, Wega Trisunaryanti* , Desinta Dwi Ristiana and Lathifah Puji Hastuti
, Desinta Dwi Ristiana and Lathifah Puji Hastuti
Department of Chemistry, Universitas Gadjah Mada Sekip Utara Bulaksumur, Yogyakarta, Indonesia.
Corresponding Author E-mail: wegats@ugm.ac.id
DOI : http://dx.doi.org/10.13005/ojc/350219
Article Received on : 17-01-2019
Article Accepted on : 12-03-2019
Article Published : 17 Apr 2019
Kinetic study of liquid product formation from hydrocracking of α-cellulose using Ni and Pd supported on Mordenite (MOR) catalysts had been conducted. The hydrocracking was performed in a semi-batch reactor with hydrogen flow (30 mL min-1). The catalysts were prepared by wet impregnation. The catalysts were characterized using Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR), X-Ray Diffractometer (XRD), Scanning Electron Microscope-Energy Dispersive X-Ray Spectrometer (SEM-EDX) and Inductively Coupled Plasma-Emission Spectroscopy (ICP-ES). Liquid product formed in hydrocracking of α-cellulose was measured under time variations of 30, 60, 90, and 120 min. at 450°C for each catalyst. The results showed that impregnation of metals increased the acidity and didn’t damage the crystallinity of MOR. The kinetics of liquid product formation using MOR, Ni/MOR and Pd/MOR catalysts followed the first order reaction with rate constant of liquid product formation (kL) of 0.0050, 0.0180 and 0.0069 min-1, respectively.
KEYWORDS:α-cellulose; Hydrocracking; Kinetics; Mordenite
Download this article as:| Copy the following to cite this article: Triyono T, Trisunaryanti W, Ristiana D. D, Hastuti L. P. Kinetic Study of α-cellulose Hydrocracking Using Ni and Pd Supported on Mordenite Catalysts. Orient J Chem 2019;35(2). |
| Copy the following to cite this URL: Triyono T, Trisunaryanti W, Ristiana D. D, Hastuti L. P. Kinetic Study of α-cellulose Hydrocracking Using Ni and Pd Supported on Mordenite Catalysts. Orient J Chem 2019;35(2). Available from: https://bit.ly/2V4dsHS |
Introduction
Hydrocracking reaction can be carried out thermally or catalytically. The thermal hydrocracking reaction took a longer time to convert the feed into fractions with light carbon compounds.1 The addition of catalyst in the cracking process will decrease the decomposition temperature so that it will lead to more efficient process.2 The catalyst used in hydrocracking can be a bifunctional catalyst comprising a metal carrying on a carrying material. Trisunaryanti et al. (2012) compared mordenite and Y-zeolite activities for the hydrocracking of tires, and proved that mordenite had higher activity than Y-zeolite.3 Mordenite, because of its uniform, small pore size, high internal surface area, flexible framework, and controlled chemistry, was widely used in catalysis, separation and purification.4 Mordenit had been proved that it could be used as catalyst in hydrocracking process to convert low density polyethylene (LDPE) and tire waste to fuel fractions.5,6,7
The concept of a bifunctional catalyst had two active sites, in which the metal on the surface of supporting material act as an active site provides the hydrogenation/de-hydrogenation process and another site acted as acid sites that provided cracking reactions.8,9 The interaction between metal and supporting material provided a very crucial role to increase catalytic performance and as a key factor in the dispersion, stabilization, and active side activity of the catalyst.10 The Ni metal selected for its high stability, low price and great availability.11 The use of Ni as a catalyst had been widely studied because it had good catalytic activity and cheap price. In addition, Ni catalysts had an advantage that was relatively high during reaction and can easily be recycled due to its magnetic properties.12 The Pd metal had good chemical stability, thus acting as a good hydrogen adsorbent medium in hydrogenation reaction.13 The effect Pd metal on mordenite and clinoptilolite had been studied and showed that Pd density increased significantly on zeolite surface area.14
In the bifunctional catalyst system, the reactant was dehydrogenated on the metal side, then diffuses at the Brønsted acid site so that it can be protonated into carbonium ions. The carbonium ion formed will undergo rearrangement or may create β-scission to form carbonium ions with shorter chains. The carbonium ion further diffused to the metal side and undergoes hydrogenation.15
Kinetic studies considering each compound and all the possible reactions were complex due the huge number of hydrocarbons involved. However, they permitted a mechanistic description of hydrocracking based on the detailed knowledge of the mechanism of the different reactions. Most of the times, applying this method to hydrocracking of real feeds was difficult because of analytical complexity and computational limitations.16
Shafizadeh (1982) first conducted a kinetics study of cellulose conversion through two approaches: intermediate reactions between the starting material and the final product, and the formation of two end products i.e. volatile and coke products.17 Burnhan et al. (2015) approached through reacting fractions and volatile products. The kinetic model proposed followed one-order reaction.18 Knowledge of chemical kinetics in degradation of solid compounds became a very important stage in the making of optimal reactor design and operation. By knowing the value of the constant rate of reaction it can be obtained an estimate value of the resulting conversion.29 Although many reviews on hydrocracking had been published, kinetic aspects in hydrocracking had not received too much attention.
Lignocelluloses consist of 40-50% cellulose, 20-40% hemicellulose, and 20-30% lignin. Cellulose which was the main constituent of lignocellulose made it very crucial in the production of fuel and chemicals.20 The cellulose crystal structure as well as the intermolecular and intramolecular hydrogen bonds made the cellulose difficult to dissolve in water as well as other conventional solvents. This problem induced a new challenge to produce fuel and chemicals directly from cellulose.2
Based on the explanation above, the author investigated kinetic study of liquid formation of α-cellulose hydrocracking using Ni and Pd metals supported on mordenite as catalysts was carried out by measuring the formation of liquid product at time variations of 30, 60, 90, 120 minutes.
Experimental Section
Materials
α-cellulose powder and methanol 98% were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich, Mordenite (HSZ 640-HOA) was purchased from Catalyst & Chemical InD.Co.Ltd., NiCl2∙6H2O and PdCl2 (with 59% Pd) were purchased from Merck.
Instrumentation
FTIR series Shimazu prestige 21, X-ray diffraction (XRD) series Rigaku Miniflex 600, Scanning electron microscope with Energy Dispersive X-Ray Analysis (SEM-EDX) series JEOL JSM-6510LA, ICP-ES series Shimadzu ICPE-9820.
Procedure
Catalyst Preparation and Characterization
Metals (Ni and Pd) were loaded onto Mordenite (MOR) and were prepared by wet impregnation method using metal salt solution. Solution was filtered and evaporated at 100°C, after that calcinated at 450°C for 3h and continued by reduction (20 mL min-1 hidrogen flow) for 3h producing Ni/MOR and Pd/MOR catalysts. The crystallinity of MOR, Ni/MOR and Pd/MOR was investigated by XRD. Surface morphology of catalysts was analyzed using SEM. The metal content on catalyst was investigated using EDX and ICP-ES. Catalysts powder were pelleted using KBr and were analyzed at 4000-300 cm-1 using FTIR.
Kinetic Study of Liquid Poduct Formation
α-cellulose and catalyst in a weight ratio of 10:1 were loaded in a semi-batch reactor (h: 30.0 cm; l: 30.0 cm; o.d.: 4.50 cm; i.d.: 3.75 cm). The reaction time was varied for 30, 60, 90, and 120 min at 450°C for 4h with 30 mL min-1 hydrogen flow. The reactor was connected with condenser and the liquid product was collected in an ice-bath system.
Results and Discussion
Catalyst Characterization
Catalyst characterization were analyzed with FTIR, XRD, SEM-EDX and ICP-ES from our previous study.22 Based on FTIR analysis indicated that the amount of acid sites increased after metals (Ni and Pd) impregnated on mordenite. Total acid sites of MOR, Ni/MOR, and Pd/MOR were 0.48; 2.46; and 4.75 mmol g-1. The XRD analysis showed that there was no damage structure in the MOR after the metals impregnation, indicating that no crystalline transformations occurred during the impregnation of metals onto Mordenite. Based on the SEM image there was no changing in the surface morphology of the catalyst after the impregnation of metal on the mordenite. This result indicated that no crystalline transformations occurred during the impregnation of metals onto the mordenite. Based on ICP-ES analysis, metal impregnated on mordenite catalyst was 0.32 wt.% and 0.50 wt.% for Ni/MOR and Pd/MOR respectively.
Kinetic Study
The catalyst and feed were placed on different lumps, the catalyst was located above the feed and separated by wire net. The feed would evaporate when the heating energy provided was sufficient, the feed vapour reached catalyst and catalytic reaction occured. The catalyst would speed up the cracking process so that the liquid product would flow out of the reactor and reached the condenser. Products with smaller molecular mass and smaller C atoms could not be condensed into liquid products and exited the reactor system as a gas product.
Effect of feed evaporation on the reactor system used in this study was only caused by the heat given when it did not reach catalyst yet. The liquid product formation occurred when cleavage of the feed formed high boiling point compounds so that it can be condensed and became a liquid product (P). The number of liquid product yields will be proportional to the reaction time (t) till reached the maximum reaction. The unevaporated feed became the residue (A). The formation of a liquid product over time can be modelled through a kinetics study of liquid product formation that resulting rate constants formation of liquid product (kL). Based on Table 1. Pd/MOR catalyst had higher liquid product than MOR and Ni/MOR catalysts at every time variation. Ni/MOR catalyst showed good performance eventhough at the early reaction liquid product formed was lower than MOR catalyst. Hydrocracking using Pd/MOR catalyst probably formed mainly gaseous product than liquid product. This may be caused by the excellent activity of palladium catalyst,23-25 this may related to the ring structure of α-cellulose.
Table 1: Liquid product formed at time variations.
|
Catalyst |
Liquid Product (g) |
|||
|
30 min |
60 min |
90 min |
120 min |
|
|
Mordenite |
0.1942 |
0.2515 |
0.2630 |
0.3565 |
|
Ni/MOR |
0.0814 |
0.1215 |
0.2493 |
0.3966 |
|
Pd/MOR |
0.2289 |
0.2768 |
0.3421 |
0.4257 |
The kinetic equation of liquid product formation was assumed that all the feed that was vaporized will be reached the catalyst and converted into liquid, gas and coke products. The formation of a liquid product was a catalytic reaction, only the feed undergone evaporation and reached the catalyst can be converted to liquid product. The rate constant of liquid product formation (kL) was determined by the intercept of the graphic equation.
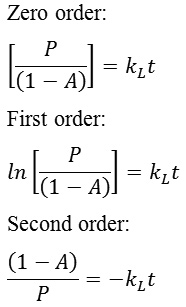
Graphics for zero order, first order and second order reaction were shown in Figure 1, Figure 2 and Figure 3 respectively. Line equations of kinetic study were shown in Table 2. The highest regression for MOR, Ni/MOR and Pd/MOR catalysts was obtained from first order graphic equation. This result represented that kinetic study of liquid product formation fitted to first order reaction for all mordenite catalysts. The rate constant of liquid product formation (kL) based on line equation was 0.0050 min–1, 0.0180 min-1 and 0.0069 min-1for MOR, Ni/MOR and Pd/MOR.
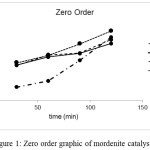 |
Figure 1: Zero order graphic of mordenite catalysts. |
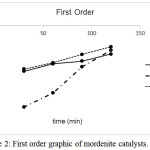 |
Figure 2: First order graphic of mordenite catalysts. |
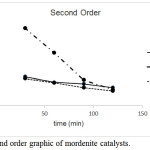 |
Figure 3: Second order graphic of mordenite catalysts. |
Table 2: Graphic equations of mordenite catalysts.
|
Catalyst |
Zero Order |
First Order |
Second Order |
|
Mordenite |
y = 0.0018x + 0.2295 |
y = 0.0050x – 1.396 |
y = -0.0141x + 3.8691 |
|
Ni/MOR |
y = 0.0046x – 0.0692 |
y = 0.0180x – 2.831 |
y = -0.0853x + 11.627 |
|
Pd/MOR |
y = 0.0029x + 0.2031 |
y = 0.0069x – 1.4175 |
y = -0.0171x + 3.8095 |
Conclusion
The kinetic of liquid product formation using MOR, Ni/MOR and Pd/MOR catalysts for α-celulose hydrocracking had been investigated. Liquid product formation followed the first order reaction with rate constant of liquid product formation (kL) was 0.0050 min-1, 0.0180 min-1 and 0.0069 min-1 respectively.
Acknowledgements
The authors thanks The Indonesian Ministry of Research, Technology, and Higher Education for Financial support. This research was conducted under research grant of PTUPT 2018 Universitas Gadjah Mada (Contract Number: 1922/UN1/DITLIT/DIT-LIT/LT/2018.
References
- Zhao, Y.; Yu, Y. J. Fuel. Process. Tech. 2011, 92, 977-982
- Sie, S.T. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res.1993, 1, 1881-1889.
- Trisunaryanti, W.; Triyono, T.; Wijaya, K.; Majid, A.B.; Priastomo, Y.; Febriyanti, F.; Hasyyati; Nugroho, A. 2012, Prosiding Seminar Nasional Kimia Unesa 2012 – ISBN : 978-979-028-550-7.
- Beeckman, J.N.; Froment, G.F. Eng. Chem. Fundam. 1979, 18, 245
- Trisunaryanti, W.; Triyono, T.; Wijaya, K.; Majid, A.B.; Priastomo, Y.; Febriyanti, E.; Syafitri; Hasyyati; Nugroho, A. 2012, Prosiding Seminar Nasional Kimia Unesa, ISBN: 978-979-028-550-7.
- Trisunaryanti, W.; Triyono, T.; Armunanto, R.; Falah, I.I.; Sriningsih, W.; Garby, M. Procedia Enviromental Sciences 2014, 20, 215-224
- Trisunaryanti, W.; Purwono, S.; Putranto, A., Indones. J. Chem., 2010, 342-347
- Scherzer, J.; Gruia, A.J. 1996, Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York
- Hayes, D. Catal. Today 2009, 145, 138-151
- Chang, F.W.; Kuo, M.S.; Tsay, M.T.; Hsieh, M.C. Appl. Catal. A 2003, 247, 309-320
- Wang, S.; Lu, G.Q.M. Appl. Catal. B 1998, 16, 269-277.
- Jianga, K.; Shenga, D.; Zhanga, Z.; Fua, J.; Houc, Z.; Lua, X. Catal. Today 2016, 274, 55-59
- Chen, Y.Z.; Wang, Z.U.; Xu, Q.; Yang, Q.; Jiang, H.L. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 10419-1042
- Korkuna, O.; Leboda, R.; kubiszewska-Zießba, J.; Vrublevs’ka, T.; Gun’ko, V.M.; Ryczkowski, J. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2005, 87, 243-254
- Weitkamp, J. ChemCatChem. 2012, 4, 292-306
- Ancheyta, J.; Sánchez, S.; Rodríguez, M.A. Catal. Today 2005, 109, 76-92
- Shafizadeh, F. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolisis 1982, 3, 282-305
- Burnhan, A.K.; Zhou, X.; Broadbelt, L.J. Energy Fuels 2015, 29, 2906-2918
- Froment, G.F.; Waugh, K.C. 1999, Elsevier Science, Amsterdam
- Geboers, J.; Vyer, S.V.; Carpentier, K.; Jacobs, P.; Sels, B. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 2167-2174
- Zhang, J.; Li, J.B.; Wu, S.B.; Liu, Y. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. . 2013, 52, 11799-11815
- Trisunaryanti, W.; Triyono, T.; Armunanto, R.; Hastuti, L.P.; Ristiana, D.D.; Ginting, R.V. Indones. J. Chem. 2018, 18 (1), 166-172.
- Chen, L.; Wang, X.; Guo, X.; Guo, H.; Liu, H.; Chen, Y. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2007, 62 (16), 4469–4478
- Yang, Q.; Chen, Y.Z.; Wang, Z.U.; Xu, Q.; Jiang, H.L. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51 (52), 10419–10422
- Xu, C.; Shen, P.K.; Liu, Y. J. Power Sources 2007, 164 (2), 527–531.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









