Deterioration in Drinking Water Resources and Relative Health Hazards in Bikaner city, Rajasthan, India: A physicochemical analysis
Yogita yadav1 Rajendra Singh2
1Department of Chemistry, RPS College of Engg. & Tech. Mohindergrah ,Haryana, India 2Department of Chemistry , Ganpati Institute of Science Technology and Management, Jaipur,Rajasthan , India
DOI : http://dx.doi.org/10.13005/ojc/290455
Article Received on :
Article Accepted on :
Article Published : 16 Jan 2014
Various kind of human development is resulting in different kind of pollution to the water resources . Monitoring of Drinking water quality and its serious analysis is very significant relative to access the human health hazards. This paper is an attempt for the same purpose . The sample were collected from main areas of the Bikaner City and were analysed for the desired physiochemical parameters applying the internationally valid standard methods. Results were compared with the international standards. It was found that drinking water quality is very poor leading to very dangerous health hazards as the most of the samples were not found to be fit on international drinking water standards. This study suggests a need to revise a more advance drinking water resources development and public health awareness policy and in depth research.
KEYWORDS:TDS; EC.; chlorides; fluorides; nitrates; total hardness. BOD; TS; TSS; physiochemical parameters; drinking water quality etc. TH= Total Hardness, TA= Total Alkalinity, DO=Dissolved Oxygen, COD=Chemical Oxygen Demand, BOD=Biochemical Oxygen Demand, Temp=Temperature, Cond. =Conductivity, TS=Total Solids, TDS=Total Dissolved Solids, TSS=Total Suspended Solids All the parameters measured as mg/L except Temperature (°C) and Conductivity (µs/cm)
Download this article as:| Copy the following to cite this article: Yadav Y, Singh R. Deterioration in Drinking Water Resources and Relative Health Hazards in Bikaner city, Rajasthan, India: A physicochemical analysis. Orient J Chem 2013;29(4) |
| Copy the following to cite this URL: Yadav Y, Singh R. Deterioration in Drinking Water Resources and Relative Health Hazards in Bikaner city, Rajasthan, India: A physicochemical analysis. Orient J Chem 2013;29(4). Available from: http://www.orientjchem.org/?p=1793 |
Introduction:
The drinking water quality is very significant and vital concern at present as it is related with the present and future health perspective of the human race. Urban population of Bikaner city is mainly dependent on govt. water supply and self boreholes as the city falls in desert area of the western Rajasthan India. Government uses bore wells and Indira Gandhi canal water for this purpose . There is heavy Industrial development in Bikaner City and these water resources are being contaminated and polluted by various modes from a several decades resulting in current early and delayed health hazards for the human population residing in this city.
Thereof this research work an attempt was made to access the physiochemical analysis of the drinking water and the related human health hazards in the selected area.
Experimental:
Drinking water samples of different locations at Bikaner city area was collected and studied during the period from may 2011 to August 2012. Electrical conductivity values were measured using systronics conductivity meter. Total alkalinity was evaluated by titration with standard 0.1M HCl using methyl orange and phenolphthalein as indicators1. Standard procedures[2-5] involving spectrophotometry, flame photometry and volumetry were used for the determination of water quality parameters. All the chemicals used were of AR grade.
Results and discussion:
Total 22 no. of water samples were analysed most of the samples were found to be alkaline due to presence of carbonates and bicarbonates and other temporary hardness. PH was find to be in the range of 7.6 to 8.5 this may result in the releasing of the toxic heavy metals like Zn , Pb, Cd And Cu , Fe etc from the supply pipes. A higher alkalinity also results in the deteriorating palatability of the drinking water. However all the sample pH were found to be within the prescribed limit of the WHO (6.5 –8.5). Total Hardness of water depends upon the amount of calcium and magnesium and other ions.
A high Magnesium concentration causes nausea, muscular neuropathy and paralysis in human body when it reaches a level of about 400mg/L8.Magnesium value in the studied area varied between 14-78 mg/L.
DO value in the studied area varied between 2.1-5.2 mg/L. 09 sampling points showed higher DO values than the prescribed limit by WHO. High amount of
DO imparts good palatability to water. BOD value in the studied area varied between 1.8-7.2 mg/L. All sampling points showed BOD values within the limit prescribed by WHO. Ground water with high value of BOD is due to microbial activities related to the bulk industrial effluents dumpsites. The old damaged supply pipe may also contribute to this factor.
Hardness value in the studied area varied between 223-678 mg/L. 4 sampling points showed higher hardness values than the prescribed limit by WHO. Alkalinity is due to the presence of bicarbonate, carbonate and hydroxide compounds calcium, sodium and potassium. Alkalinity itself is not harmful to human beings4. Alkalinity value in the studied area varied between 196-665 mg/L. 9 sampling point showed alkalinity value within the limit prescribed and 13 sampling area showed higher alkalinity values than the prescribed limit by WHO.
Conclusion:
According to WHO, nearly 80% of all the diseases in human beings are caused by water10-11.The water quality parameters of the various areas of Bikaner city Rajasthan indicates that the drinking water samples are not fit on the standard parameters and the quality is poor for drinking purpose. After purification treatment only this water can be used for drinking. The values of correlation coefficients will help in selecting proper treatment to minimize pollution. Drinking water pollution in the studied area should be controlled by the proper environment management plan to maintain proper health conditions of people.
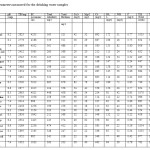 |
Table no-1 : Parameters measured for the drinking water samples Click here to View table |
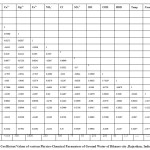 |
Table 2 Correlation Coefficient Values of various Physico-Chemical Parameters of Ground Water of Bikaner city ,Rajasthan, India Click here to View table |
References:
- APHA . Standard methods for the examination of water and waste water (19th ed) (1996).
- Nagarajan S, Swaminathan M and Sabarathinam PL, “Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater” Poll. Res., 12(4): 245. (1993). Washington, DC: Public Health Association.
- M. Hussain, T.V.D.P. Rao, H.A. Khan and M. Satyanarayan. “Chemical Properties of Drinking Water of Some Villages in Sangamner Tahasil, Dist- Ahmednagar, Maharashtra, India and its Impact on Human Health” , Orient. J. Chem., 27(4): 1679- 1684 (2011).
- A. Malviya, S.K. Diwakar and S.O.N. Choubey. “Chemical assessment of narmada river water at Hoshangabad city and Nemawar as navel of river in Central India” ‘ Orient. J. Chem. 26(1): 319-323 (2010).
- Trivedy R K and Goel P K, “Chemical and Biological Methods for Water Pollution Studies”, Environmental Publications, Karad, 7: (1986)
- Surve P R, Ambore N E and Pulle J S, “Ground Water Quality of Gandhinagar Taluka, Gujarat, India” Eco.Env. and Consv., 8(1): 87-90 (2005).
- M.G. Adak, and K.M. Purohit, “Chemical Properties of Drinking Water of Some Villages in Sangamner Tahasil, Dist- Ahmednagar, Maharashtra, India and its Impact on Human Health” Poll. Res., 20: 575 (2001).
- C. H. Srinivas, Ravi Shankar Piska, C. Venkatesan, M. S. Sathya Narayana Rao, and R. Ravinder Reddy, “Chemical Properties of Drinking Water of Some Villages in Sangamner Tahasil, Dist- Ahmednagar, Maharashtra, India and its Impact on Human Health” Poll. Res., 19(2): 285 (2000).
- APHA, “Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater”, American Public Health Association, Washington D.C.,(1998).
- G. Dilli Rani, M. Suman, C. Narasimha Rao, P. Reddi Rani, V. G. Prashanth, R. Prathibha and P. Venkateswarlu “Physico- chemical analysis of underground drinking water in jorve, tahasil sanganer , Dist- ahmednagar Maharashtra, India” Current World Environment, 6 (1): 191-193 (2011) .
- P. Venkateswarlu, M. suman and C. Narasimha Rao, Research Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical Sciences, 2(2): 464-469 (2011).

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









