New D-glucopyranosyl -6-α-4’- methoxy Rhamnopyranoside from Cyathula tomentosa
Dwarika Prasad
Department of Chemistry Lovely Professional University Punjab (India)
DOI : http://dx.doi.org/10.13005/ojc/290356
Article Received on :
Article Accepted on :
Article Published : 28 Oct 2013
From ethanolic extract of Cyathula tomentosa plant new D-glucopyranosyl -6-α-4’- methoxy rhamnopyranoside and new 5,7-dihydroxy, 13,14-dimethoxy flavanone have been isolated and characterized with help of FAB mass, 1H, 13C NMR, HMQC .
KEYWORDS:Cyathula tomentosa;D-glucopyranosyl -6-α-4’- methoxy rhamnopyranoside;5,7-dihydroxy
Download this article as:| Copy the following to cite this article: Prasad D. New D-glucopyranosyl -6-α-4’- methoxy Rhamnopyranoside from Cyathula tomentosa . Orient J Chem 2013;29(3). doi : http://dx.doi.org/10.13005/ojc/290356 |
| Copy the following to cite this URL: Prasad D. New D-glucopyranosyl -6-α-4’- methoxy Rhamnopyranoside from Cyathula tomentosa . Orient J Chem 2013;29(3). Available from: http://www.orientjchem.org/?p=374 |
Introduction
Cyathula tomentosa (Kurru) belongs to family Amaranthaceae, is a perennial under shrub occurs throughout Garhwal Himalayas up to 600-2000 meter altitude, Cyathula tomentosa has been used in snake bite and has emetic properties [1]. From Cyathula capitate and Cyathula officinal ecdyson content as 0.046% and 0.057% isolated respectively [2] and Cyathula prostrata show antifungal free radical scavenging activities 2,2-diphenyl-1-picryl hydrazyl [DPPH] radical [3]. The chemical examinants at the basis of [4] has been reviewed. From ethanolic extract of cyathula tomentosa a new Disaccharide has isolated. The structure of compounds have been elucidated through. mass, 1H, 13C NMR and HMQC spectra.
Experimental
General: 1H-NMR at (400 MHz),13C-NMR at (75 MHz) TMS as internal standard, using DMSO as solvent column chromatography was carried out on silica-gel 60-120 mesh (Merck). TLC was performed on percolated silica-gel. The eluting solvent was CHCl3-MeOH spots were visualized by 7% H2SO4 followed by heating.
Plant material: The whole plant of Cyathala tomentosa was collected from Bacchear District. Chamoli Uttrakhand in the month of October and identified by Department Botany, P.G. College Gopeshwar where voucher specimen was deposited.
Extraction and isolation: The air dried whole plant (3kg) was exhaustively extracted with 95% aqueous ethanol at 30-500C (for 48 hours) on a heating mantle. The ethanol extract was concentrated to dryness under reduced pressure to yield a black brown residue(200g) and then adding to the top of the column prepared using 500g silica gel(60-120 mesh; Merch, Mumbai, india) in chloroform. The dry ethanolic extract was chromatographic over silica-gel using Methanol:Chloroform elution solvent at (30:70) afforded a new disachride.
Result and Discussion
Compound was crystallized from methanol as colorless crystalline solid. On the basis of elemental analysis the molecular formula deduced as C13O10H24. The molecular weight of the compound as shown from its FAB-MS is 356 amu, as the spectra was giving molecular ion peak at m/z 357 and fragment peaks 136, 180, 192 etc.
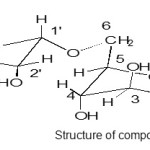 |
Structure of compound Click here to View figure |
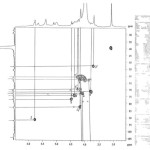 |
Figure: Click here to View figure |
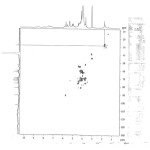 |
Figure Click here to View figure |
The 13C-NMR Spectrum of the compound showed the presence of 13 carbons signals; six peaks at δ 91.78 , 77.13, 72.9, 62.13, 74.87, 62.14 were correlated with D-glucopyranoside and six peaks at δ 104.07, 69.89, 71.67, 82.57, 60.5, 29.0 for α – rhamnopyranoside and one peak at δ 52.5 for methoxy group attached at C-4′ which appeared on the downfield from the normal value. These value were again confirmed by 1H NMR spectra the presence of singlet at δ 5.78 indicated anomeric signal and doublet at δ 4.13 [J=2.3Hz]for H-2 with other multiple peaks at δ 4.59, 3.7, 4.54, 4.1 for H-3, 4, 5, 6 respectively for D-glucopyranoside and singlet at 5.47 for anomeric proton of α- rhamanopyranoside doublet at δ 4.2 (J =9.2Hz) for H-2′ and other multiple peak at δ 3.76, 4.32, 4.40, for H-3′, 4′, 5′ and singlet at 1.86 for H-6′ or methyl group of ramose and one singlet at 3.59 for methoxy group and singlet at δ 5.75, 5.1, 5.2 for OH groups also α -configuration further confirmed by acidic hydrolysis (7%MeOH-HCl, 10ml, 60to800C, 8hr) furnished 4′-methoxy rhamanose and D-glucose confirmed by Rf values(PC) and co-TLC by direct comparison of authentic sample . These peaks values further confirmed by HMQC as in following spectra.
The characterized compound was again compared with the spectral data of the closely related compound as appeared in the literature [4] and it was identified as D glucopyranosyl -6-α-4’methoxy rhamnopyranoside.
Acknowledgement:-
Thanks are due to SAIF, CDRI-Lucknow for recording spectra.
References
- Gaur R.D, Flora of District Garhwal North West Himalaya (With EthnobotanicalNotes), 1st ed.(Trans Media, Srinagar Garhwal, india., 1999.
- Shu Y, Zou Z and Yang A. Plant Medica 14:37 (1992).
- Cavin A and Dyatmyko W. Pharm. Biology. 37[4]:260 (1999) .
- Malikov V.M. and Yuldashev M.P. Khim. Prir. Soedin. 5:385 (2002).
- C H Cony, M P Lyne and M J Grange; Microbiological Methods, 7th ed, Butter worth-Heinemann. Ltd, Great Britain (1995).

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









