Polymorphisms in DNA Sequence and Personalized Alternative Herbal Drugs
Dayadhar Dikshit*
*Department of Chemistry, Pt. L. M. S. Gov. (Autonomous) P. G. College, Rishikesh - 249 201, India.
Currently doctors diagnosis the disease and prescribe medicine on the basis of external symptoms and blood report of the patient. It some times results adverse effect, overdose of medicine. Adverse drug reaction accounted for 2.2 million hospitalizations and over 1,00,000 deaths in USA in 19941. Currently there no simple way to determine whether people will respond well, badly, or not at all to a medication. Pharmacogenomics2 deals with the influence of genetic variation on drug response in patients by correlating gene expression or single nucleotide polymorphism with a drug’s efficacy or toxicity. Therefore it provides a revolutionary pathway to diagnosis the disease and prescribes “Personalized” medicine on the basis patient’s genotype. Genetic variation in drug receptors can have a profound effect on drug efficacy. It has been already reported that variation in sequence of amino acid in DNA directly affects the response of β2 – adrenoreceptor to β2 – agonists3-4. In this paper we discusses polymorphism in DNA and its effect on synthesis of drug metabolizing enzymes in human beans and other organism and it’s use to determining the doze of alternative herbal drugs for patient along with benefits, challenges and various research scope in pharmacogenomics.
KEYWORDS:Pharmacogenomics; polymorphism; β2-agonists; alternative herbal drug
Download this article as:| Copy the following to cite this article: Dikshit D. Polymorphisms in DNA Sequence and Personalized Alternative Herbal Drugs. Orient J Chem 2013;29(1). |
| Copy the following to cite this URL: Dikshit D. Polymorphisms in DNA Sequence and Personalized Alternative Herbal Drugs. Orient J Chem 2013;29(1). Available from: http://www.orientjchem.org/?p=25194 |
Introduction
Herbal medicines are a part of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM); Ayurveda, and other healthcare systems such as homeopathy. Herbal drugs are considered as less potent than prescribed medicines. The latter usually contain one highly concentrated active ingredient, while herbs may have several active ingredients that are chemically similar. Herbal ingredients work synergistically to contribute to, or detract from, the therapeutic effect of each individual ingredient. Natural herbs are nothing more than plants made by the God, with Infinite Intelligence, therefore they have no harmful side-effects.The man-made, synthetic drugs stop, block or replace a bodily function while herbs work with the body’s natural functions. Man-made drugs usually work on relieving the “symptoms” of a disease, whereas herbs work on the cause of the disease. Since herbs are natural, they are more readily absorbed and assimilated by the body. Since man-made drugs are unnatural, the body doesn’t recognize them, so only a small amount are actually absorbed and assimilated. Whether human-made or natural, the most important criteria for a medicine’s use is safety, effectiveness and quality: identity, purity, potency and stability. Therefore drug doze is also an important matter of discussion and research. Currently doctors diagnosis the disease and prescribe medicine on the basis of external symptoms and blood report of the patient and there are no simple way to determine whether people will respond well, badly, or not at all to a medication. Therefore pharmaceutical companies are developing drugs using a “one size fits to all” system. Latest researches show that inter individual differences in drug response is also depends on variation in gene encoding drug-metabolizing enzymes, drug transporters or drug targets5-8. It has been already reported that variation in sequence of amino acid in DNA directly affects the response of b2 – adrenoreceptor to b 2 – agonists7-8.
Single Nucleotide Polymorphism and its effect on drug responce
A Single Nucleotide Polymorphism, or SNP, is a small genetic change, or variation, that can occur within a person’s DNA sequence. More then 1.4 million SNPs were identified in initial sequencing of human genome.
The genetic code is specified by the four nucleotide, A (adenine), C (cytosine), T (thymine), and G (guanine). SNP variation occurs when a single nucleotide, such as an A, replaces one of the other three nucleotide letters—C, G, or T. The alteration of the DNA segment AAGGTTA to ATGGTTA, where the second “A” in the first snippet is replaced with a “T”. If SNPs found within a coding sequence are of particular interest to researchers because they are more likely to alter the biological function of a protein.
For example
Variation in sequence of amino acid in DNA directly affects the response of b2 – adrenoreceptor (a gene product) to b 2 – agonists (medicine) in humans.
Variation in sequence of amino acid in DNA that code CYP450 enzymes can influence their ability to metabolize certain drugs. Less active or inactive forms of CYP enzymes can cause drug overdose in patient.
The enzyme;MRD-1 acts on Anticancer drugs and decreased response in HIV Infected patients, therefore high dose of medicine is required for such patients
Gs protein a acts on b-lockers such as metoprolol and results in antihypertensive effect.
The enzyme; N-acetyltransferase (NAT2) acts on Isoniazid, caffin and sulfonamides drugs and make patients, Hypersensitivity for these drugs therefore even low dose of medicine effects as over doze.
Similarly SNP influence various other enzymes and hence drug response. Beside these enzyme drug transport proteins also affected by SNP and influence various drug response. They provide protective functions (Blood-brain barrier), contributing to critical cellular processes and Influence drug absorption from small intestine.
Alternative herbal drugs
Caffeine
Caffeine is reliable herbal alternative of synthetic drug, Isoniazid. Isoniazid (Laniazid, Nydrazid)is , also known as isonicotinylhydrazine (INH), is an organic compound that is the first-line medication in prevention and treatment of tuberculosis. Isoniazid is available in tablet, syrup, and injectable forms (given intramuscularly or intravenously and may be prepared by the base hydrolysis of 4-cyanopyridine to give the amide, followed by displacement of ammonia byhydrazine9.
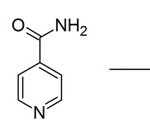 |
Scheme 1 Click here to View schem |
This medicine causes very serious liver disease. Therefore the effect of it’s herbal alternative ‘Caffeine’ along with polymorphism in DNA sequence is subject matter of discussion.
Ephderine
It is reliable herbal alternative drug of b 2 – agonists7 it includes Clenbuterol and Salbutamol. Medically these drugs are used to reduce the symptoms caused by asthma.
References
- J. Lazarou, B.H. Pomeranz and P.N. Corey, JAMA., 279 (15), 1200 (1998).
- J.E. Staunton, D.K. Slonim, H.A. Coller et al., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA.,98, 10787 (2007)
- S.B. Liggett,Am.J. Respir. Crit. Care. Med., 161,S 197 (2000).
- J.O. Khatri, Pharma. Times, 11,28 (2006).
- W.E. Evans and H.L. McLeo,N.Engl.J.Med.,348, 538(2003)
- W.E. Evans and M.V. Relling,Science,286, 487(1999)
- P.E.Carson, C.L. Flanagan, C.E. Ickes and A.S. Al-ving, Science,124, 484(1956)
- W.E. Evans,Gut.,52ii, 10(2003).
- T. P. Sycheva, T. N. Pavlova and M. N. Shchukina (1972). “Synthesis of isoniazid from 4-cyanopyridine”.Pharmaceutical Chemistry Journal6 (11): 696–698.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









