Physico-Chemical Characteristics of Toothpastes and Natural Powder and Study Their Antibacterial Activity Against Viridans Streptococci Bacteria
Karzan A. Omar1, Awara K. Ismail2, Chnar M. Amin1, Mardin S. Jalal1, Sebar N. Qadr1 and Zaynab F. Rafiq1
1Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science and Health, Koya University, University Park, Danielle Mitterrand Boulevard, Koya KOY45, Kurdistan Region of F.R. Iraq.
2Department of Biology, Faculty of Science and Health, Koya University, University Park, Danielle Mitterrand Boulevard, Koya KOY45, Kurdistan Region of F.R. Iraq.
Corresponding Author E-mail: karzan.abdulkareem@koyauniversity.org
DOI : http://dx.doi.org/10.13005/ojc/330553
The physical-chemical characteristics of several kinds of toothpaste and natural powder samples and their antibacterial activity against Viridans streptococci bacteria have been studied in vitro. The physical-chemical analysis such as pH, conductivity, and moisture and fluoride concentration of the toothpaste and natural powder along with X-Ray Diffraction made in the consideration to indicating the quality of toothpaste and natural powder products. The results of the physical-chemical properties revealed the differences between toothpaste and natural powder samples. The toothpaste samples exhibited very good antibacterial activities against Viridans streptococci bacteria in comparison to the natural powder almost have no activity against bacteria.
KEYWORDS:Toothpaste; Natural Powder; Physical-Chemical Properties; Viridans Streptococci
Download this article as:| Copy the following to cite this article: Omar K. A, Ismail A. K, Amin C. M, Jalal M. S, Qadr S. N, Rafiq Z. F. Physico-Chemical Characteristics of Toothpastes and Natural Powder and Study Their Antibacterial Activity Against Viridans Streptococci Bacteria. Orient J Chem 2017;33(5). |
| Copy the following to cite this URL: Omar K. A, Ismail A. K, Amin C. M, Jalal M. S, Qadr S. N, Rafiq Z. F. Physico-Chemical Characteristics of Toothpastes and Natural Powder and Study Their Antibacterial Activity Against Viridans Streptococci Bacteria. Orient J Chem 2017;33(5). Available from: http://www.orientjchem.org/?p=37512 |
Introduction
Toothpaste is one of important care products which are necessary for healthy teeth and oral hygiene. Toothpaste was made for teeth cleaning and protecting the mouth from oral microorganism. The ingredient in toothpaste been improved by adding antimicrobial agents such as zinc oxide, titanium oxide, tin oxide and their composites1 to eliminate and inhibit microbial growing which mostly causes for tooth decay and other oral diseases2. Also, fluoride is one of the most significant active ingredients in the toothpaste have the effective ability to clean and deciduous teeth3. In the dental care fluoride working under the mechanism to inhibiting carbohydrate fermentation by bacteria in the oral cavity and preventing aggregation of bacteria by disrupting their cell walls and inhibiting their enzymatic activity 4,5. The commercial toothpaste contains different concentrations of fluoride, which is varied from 1000 to 1450 ppm and this range depend on people age. But despite it is advantages, also it has disadvantages. If the fluoride concentration excess than acceptable level, causing to cells to die and brittle teeth which known as fluorosis6. The excessive fluoride of more than 1500 ppm can cause to poisoning, bone fragility, liver, and kidney damage7. Also, the pH of toothpaste is important to maintain the pH of the mouth in a basic medium which prevents bacteria from growth in the oral cavity.
Recently, the natural whitening powder is considered by some people as a replacement of toothpaste without knowledge of its chemical composition and element analysis, which may contain harmful elements in the used natural powder and their physical characteristics8.
The purpose of this research was studyingphysical-chemical characteristics and fluoride evaluation of several kinds of toothpaste, along with the whitening natural power and showing their activity against isolated bacteria Viridans streptococci from infected patients with the dental diseases.
Method and Materials
Analytical grade reagents and distilled water were used for solution preparations. The prepared solutions were stored in a cleaned volumetric flask and Viridans streptococci bacteria were obtained from Dental College at Hawler Medicine University. The toothpaste and natural whitening powder samples were collected randomly in the Kurdistan region market, labeled from S1 to S6 as follows Crest (S1), Signal (S2), Laculate (S3), Kin (S4), Colgate (S5), Natural whitening powder (S6) and analyzed.
Fluoride Contents
Sample preparation depended on the sample type of the sample matrix, and the form of the fluoride ion, that is, in its free or complexes form. The samples of toothpastes (1 g) were dissolved in distilled water and were quantitatively transferred to a 100 ml volumetric flask that was filled to the mark. To speed up the dissolution, the sample was heated for 15 minutes in a water bath prior to filling to the mark. Upon cooling, 4 ml 6 M HCl was added to release fluoride ions completely after that the fluoride concentration measured by Photolab S12.
Moisture Content
The toothpaste samples were weighed in crucible (5.0 grams) and heated in an oven at 105oC for 6 hours. The moisture content was calculated from the difference between the initial and final weights.
pH and Conductivity Analysis
The pH was measured using a digital pH meter (DMPH-2, Digimed; Sao Paulo, Brazil) and conductivity (Model). Measurements were performed only once for each sample at a dilution of 5.0 grams suspended in 10 ml of distilled water.
Antimicrobial Assay Using the Disc Diffusion Method
The stock solutions of toothpaste were prepared from 0.5 gm of each sample dissolved in 10 ml distilled water were absorbed on the small filter paper discs. The filter paper discs impregnated with stock solutions of each sample in the incubator at 37°C for 1 hour to dry them. The antimicrobial assay of samples was performed by disc diffusion method as described by Kirby-Bauer. Loop full growths from bacterial isolate were inoculated on chocolate agar incubated at 37°C for 18 hours. After that, transfer some bacterial colonies into 2ml normal saline to dilute with normal saline. Adjust the turbidity and compare with standard tube (McFarland number 0.5) to yield a uniform suspension. A cotton swab was dipped and streak into adjustment suspension the entire Chocolate agar and Blood agar. Sample pleats or discs were gently pressed on the surface of the agar. The plates were incubated overnight at 37°C while the antibiotic diffuses from the disc into the agar. After incubation, the plates were examined for the presence of inhibitory zones9.
Results and Discussions
Fluorides are one of the most important ingredients in the toothpaste products for oral hygiene due to their ability to prevent the tooth from decay. The fluoride concentration of study samples is shown in (fig. 1). The fluorides level in the S1, S2, and S4 were higher than the claimed level and S3 and S5 were lower than claimed level, but S6 has contained the lower level of fluorides in comparison to the rest of the samples. The hygiene of tooth is directly related to the concentration of fluorides in the toothpaste, the higher and lower levels cause to dental fluorosis.
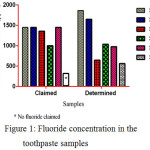 |
Figure 1: Fluoride concentration in the toothpaste samples |
The pH of toothpaste plays an important role in keeping mouth in the basic medium to prevent growing bacteria which may cause damage to our teeth such as tooth decay, cavities, and gum disease. Therefore, the pH of toothpaste samples being measured as shown in (fig. 2). It indicates most of the samples have a basic pH except S1 which has a neutral pH.
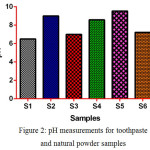 |
Figure 2: pH measurements for toothpaste and natural powder samples |
But certain types of acidic foods which have a pH below of 7 cause to lower pH and increase the acidity of saliva in the mouth, in this case, saliva require a long time to neutralize the pH of the mouth may take several minutes to hours which depend on the type of ate food. Therefore, it is necessary for mouth brushing after every meal for at least more than 2 minutes to maintain mouth medium in the basic pH as shown in (fig. 3).
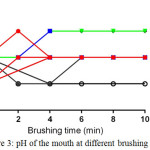 |
Figure 3: pH of the mouth at different brushing time |
Also, proper brushing and type of toothpaste has an effect on the medium of the mouth as shown in figure (3), most of the samples during two minutes, brushing maintaining mouth in the basic medium after eating except sample 6 decreases the pH mouth too acidic medium which probably provides a better environment for harmful bacteria for decay teeth.
Conductivity of Toothpaste and Natural Powder Samples
Fig. 4 Shows the conductivity of samples at room temperature. The conductivity of S4 higher than all samples due to the presence of active ions in it and conductivity of S6 lower than other samples due to the presence of less active ions in it.
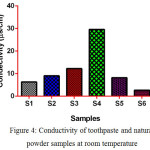 |
Figure 4: Conductivity of toothpaste and natural powder samples at room temperature Click here to View figure |
Moisture Content
The moisture content has an impact on the physical properties and quality of toothpaste. The presence of moisture in the toothpaste helps prevent dry mouth. The S3 has higher moisture contents in comparing to other samples except S6 which has lower moisture contents is shown in (fig. 5).
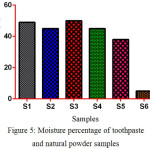 |
Figure 5: Moisture percentage of toothpaste and natural powder samples |
Humectants give toothpaste texture and help to retain moisture to keep it from drying out. Glycerin, sorbitol, and water are common humectants. Xylitol is the best type of humectant since it has multiple benefits, including increasing the flow of saliva, which helps prevent dry mouth, and also has been shown in early reports to help prevent tooth decay.
X-Ray Diffraction of Toothpaste and Natural Powder Samples
The X-ray diffraction analysis carried out for toothpaste and natural powder as shown in Table 1 and 2. The XRD indicated various elements in both samples with different percentage. But the present of heavy elements in the high percentage indicated in the natural powder in comparison to toothpaste samples, and the ratio of toxic heavy elements such as nickel and lead has been observed in the natural powder in the different percentage.
Table 1: XRD analysis of natural powder sample
|
Element oxides |
Mass% |
Element | Mass% |
| SiO2 |
47.1 |
O |
48.8 |
| CaO |
24.2 |
Si |
20.3 |
| Al2O3 |
10.6 |
Ca |
14.9 |
| MgO |
7.22 |
Al |
5.22 |
| Fe2O3 |
6.55 |
Mg |
4.11 |
| K2O |
2.08 |
Fe |
3.95 |
| TiO2 |
0.96 |
K |
1.55 |
| SO3 |
0.374 |
Ti |
0.421 |
| P2O5 |
0.312 |
P |
0.124 |
| MnO |
0.124 |
Mn |
0.0797 |
| ZnO |
0.01 |
Ni |
0.0214 |
| NiO |
0.032 |
Sn |
0.0091 |
| SnO2 |
0.0138 |
Zn |
0.0076 |
| PbO |
0.0017 |
Pb |
0.0015 |
Table 2: XRD analysis of toothpaste samples
|
Element oxides |
mass% |
Element |
mass% |
| SiO2 |
28.9 |
O |
67.2 |
| CaO |
59.3 |
Si |
8.6 |
| Al2O3 |
0.962 |
Ca |
20.9 |
| MgO |
0.476 |
Al |
0.322 |
| Fe2O3 |
0.116 |
Mg |
0.154 |
| K2O |
0.839 |
Fe |
0.0295 |
| TiO2 |
2.16 |
K |
0.474 |
| SO3 |
3 |
Ti |
0.494 |
| P2O5 |
3.68 |
P |
0.926 |
| MnO |
0.0138 |
Mn |
0.0036 |
| ZnO |
2.71 |
Ni |
0 |
| NiO |
0 |
Sn |
0.0406 |
| SnO2 |
0.123 |
Zn |
0.0802 |
| PbO |
0 |
Pb |
0 |
Activity of Toothpaste and Natural Powder Against Viridans Streptococci Bacteria
The antibacterial activity of samples studied against gram-positive bacteria the viridans streptococci. The reason of the selection such type of bacteria due to the viridans streptococci is most prevalent in the oral cavity, but also reside in the other parts of the human body. Although they are commensal organisms in these sites, these microorganisms may also invade sterile body sites, which can lead to life-threatening diseases.
The sample concentration of 0.5 mg/ml, exhibited inhibitory effects against the growth of bacteria on chocolate agar and blood agar, while the S6 at a concentration of 0.5 mg/ml showed the non-inhibitory effect against the growth of bacteria on chocolate agar and blood agar. The clear zone of inhibition around the discs was evidence of antibacterial activity of other samples as shown in (fig. 6-19). The chocolate agar used for indicating clear results of inhibition zones of samples along with the blood agar. The S1 and S2 were showed excellent antibacterial activity against the harmful viridans streptococci bacteria than the other samples.
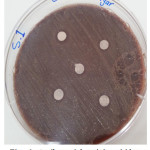 |
Figure 6: Antibacterial activity viridans Streptococci treated by S.1 on chocolate agar |
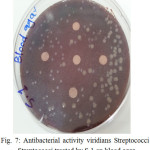 |
Figure 7: Antibacterial activity viridians Streptococci treated by S.1 on blood agar |
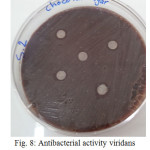 |
Figure 8: Antibacterial activity viridans Streptococci treated by S2 on chocolate agar |
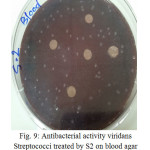 |
Figure 9: Antibacterial activity viridans Streptococci treated by S2 on blood agar |
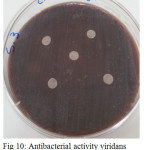 |
Figure 10: Antibacterial activity viridans Streptococci treated by S3 on chocolate agar |
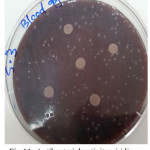 |
Figure 11: Antibacterial activity viridians Streptococci treated by S3 on blood agar |
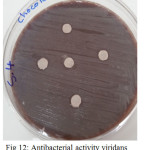 |
Figure 12: Antibacterial activity viridans Streptococci treated by S4 on chocolate agar |
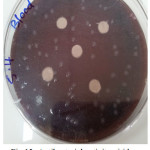 |
Figure 13: Antibacterial activity viridans Streptococci treated by S4 on blood agar |
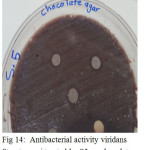 |
Figure 14: Antibacterial activity viridans Streptococci treated by S5 on chocolate agar |
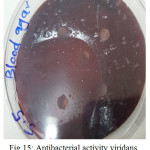 |
Figure 15: Antibacterial activity viridans Streptococci treated by S5 on blood agar |
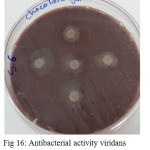 |
Figure 16: Antibacterial activity viridans Streptococci treated by S6 on chocolate agar |
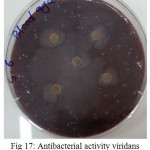 |
Figure 17: Antibacterial activity viridans Streptococci treated by S6 on blood agar Click here to View figure |
 |
Figure 18: Bacterial control viridans Streptococci untreated on chocolate agar |
 |
Figure 19: Bacterial control viridans Streptococci untreated on blood agar |
Conclusions
The physical-chemical analysis of toothpaste and natural powder samples indicated there are differences between fluoride concentrations of claimed and calculated and the fluoride concentration of natural powder is too low. The pH of samples was 6.5 to 9.8 which plays an important role to keep mouth in the healthy medium. Therefore, the brushing time has been conducted for all samples at the different time from 2 to 10 minutes to indicate better brushing time to maintain mouth in the basic medium. The active ions in the samples being measured byconductometer and moisture percentage of samples were an inappropriate ratio to prevent mouth dry during brushing except for S6. The XRD analysis for toothpaste and natural powder samples indicated the different percentage of elements in the samples and trace of toxic heavy elements in the natural powder sample. The antibacterial activity of S1 and S2 among samples was very good against Viridans streptococci bacteria and the S6 showed almost no activity against Viridans streptococci bacteria, which is indicating that the natural powder not suitable to be used instead toothpaste.
Acknowledgement
The authors are grateful to Dr. Tara Fuad Tahir, the Head of the Chemistry Department, Assistant professor Dr. Taha Jalal Omar, the Dean of the Faculty of Science and Health of Koya University for their supports and cooperation.
References
- Omar, K. A.; Meena, B. I.;Muhammed, S. A. Physicochemical Problems of Mineral Processing. 2016, 52, 754−766.
- Fine, D.H.; Furgang, D.; Markowitz, K.; Sreenivasan, P.K.; Klimpel, K.; De Vizio,W.J Am Dent Assoc.2006, 10, 1406-13.
CrossRef - Marinho, V.C.; Higgins, J.P.;Sheiham, A.; Logan, S. Cochrane Database SystRev.2009, 1, 1-15.
- Arnold, W.;Dorow, A.;Langenhorst, S.;Gintner, Z.; Bánóczy, J.;Gaengler, P. BMC Oral Health.2006, 6, 8.
CrossRef - Bou-Chacra, N.A.; Gobi, S.S.;Ohara, M.T.; Pinto, T.J. RevistaBrasileira De CienciasFarmaceuticas. 2005, 41, 323-31.
CrossRef - Susanti, P.H.; Devinta, L.;Yohanes, M. Dental Journal.2013, 46, 3.
- Sérgio., P.H.;Shelon, C. S.; Paulo, V. F.;Fábio, A. S.; Denise, S. W. Braz Oral Res. 2011, 25, 288-94.
- Jaroslava, S.G.;Zorica, S.;Ivana, V.;Isidora, K. Journal of food and drug analysis.2013, 21, 384e3 8 9.
- Hiba, J.H. World Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences.2014, 3, 65-78.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









