Calcium Ion Selective Electrode Based on Surface Modified Zeolite Based Ionophore and its Analytical Application
A. Vijayalakshmi and J. Thamarai selvi
Department of Chemistry, Avinashilingam Institute for Home Science and Higher Education for Women Coimbatore- 641043, Tamilnadu, India.
DOI : http://dx.doi.org/10.13005/ojc/330147
A new, efficient Calcium ion selective electrode has been prepared using Surface modified Zeolite based ionophore.The prepared ionophore is characterized by UV,FT-IR,XRD..The sensor exhibits a near Nernstian response for Ca(II) ion over a concentration range of 1.0 X 10-4 M to1.0 M . The proposed sensors revealed relatively good selectivity and high sensitivity for Ca(II) over a monovalent cations. It can be used with in the pH range of 5.57 to 6.24 . The effect of medium and the selectivity coefficient values was evaluated using fixed interference method found to give a better response. . It was also successfully used in the analysis of concentration of Calcium ion in various real samples.
KEYWORDS:Calcium (II); Surface modified Zeolite; Potentiometry; Selectivity coefficient
Download this article as:| Copy the following to cite this article: Vijayalakshmi A, selvi J. T. Calcium ion Selective Electrode Based on Surface Modified Zeolite Based Ionophore and its Analytical Application. Orient J Chem 2017;33(1). |
| Copy the following to cite this URL: Vijayalakshmi A, selvi J. T. Calcium ion Selective Electrode Based on Surface Modified Zeolite Based Ionophore and its Analytical Application. Orient J Chem 2017;33(1). Available from: http://www.orientjchem.org/?p=30112 |
Introduction
The introduction of new ion-selective electrodes has played a fundamental role in the development of various sensory elements according to the charge and size of the target ion in clinical and environmental assays[1-8]. Potentiometric methods using ISEs for determining the metal ion have been studied extensively due to their importance in biological process[9,10],easy handling, nondestructive analysis and in expensive sample preparation, applicability to coloured sample and turbid solution.Calcium is the major element in the body.It plays a Vital role in the formation of bone,neuro muscular function,coagulation&membrane permeability.In plants it helps in transpiration which leads to growth of the plant.
Bedlechowicz et al;2002 developed calcium ion selective electrode using ETH1001 as an ionophore.In 2004 Kumar&Mittal developed a new Calcium ion selective electrode based on PVC membrane modified by a new ionophore dibenzo-18-crown-6(DB18C6).
Taking into consideration of all the above facts that a new simple ionophore such as surface modified zeolite have been used as an electroactive phase for the fabrication of Ca2+ ion selective electrodes . In the present study the electrode show good selectivity and reproducibility over Ca2+ ion and the results are presented in this paper.
Experimental Method
Chemicals Used
Silicic acid, Reagent grade tetrapropyl ammonium bromide ,tetrahydrofuran,,Ethyl acetate,Dimethyl Acetamide,DMF, Dioctyl phthalate (DOP), sodium tetra phenyl borate (NATBP), tetra hydro furan (THF) were obtained from E.Merck and can be used without further purification. Throughout double distilled ionized water used.
Synthesis of Ionophore
2g of Silicic acid was mixed with 3.5g of tetrapropyl ammonium bromide and 0.514g of NaOH&50 ml of water.The above mixture was heated at 100°C for 5h.The white precipitate was obtained.The silica content of the precipitate was determined by evaporation method &found to be 1.1ML-1. 1g of the above precipitate was dissolved in 2 ml of water and was mixed with a1.15M aluminate solution (1ml) to adjust the Si/Al molar ratio to 0.5M.The mixed solution was heated at 80°C for 24h.The resulting reaction mixture was dried in a oven at 60°C overnight.The surface modified Zeolite was prepared by mixing the above mixture with 100mM HDTMA solution &stirred for 24h.The mixture was then centrifuged at 5000rpm for 20min&finally the mixture was dried. Yield:2.5g,Melting point:201°C
Physical Measurements
For recording UV and Visible spectrum PC based UV double beam spectrometer 2202 was used.FT-IR spctra were recorded on a FT-IR spectrometer.(model Shimadzu prestige-21 series)X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis was carried out using PANanalytical x-Pert pro diffractometer from CuKα radiation(X-Ray tube PW 3050/60),
In UV spectrum the peak at 221nm corresponds to CN group (Pavianet al; 2001)-fig-1
In FT-IR HDTMA Surfactant,,Zeolite&SMZ are shown in fig-2
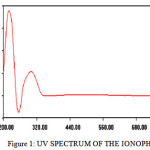 |
Figure 1: UV SPECTRUM OF THE IONOPHORE Click here to View Figure |
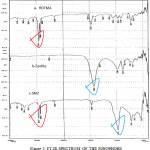 |
Figure 2: FT-IR SPECTRUM OF THE IONOPHORE Click here to View Figure |
The Zeolite absorbed frequencies are 501,802,1064,1465,1635,2376,2970,3788 and 3842cm-1
SMZ showed frequencies are 462,794,1095,1435,1627,2376,2854,2924,3425,3749,3842 which indicate the incorporation of HDTMA on the Zeolite Surface.There was a slight shift in peaks at each wave numbere speically in the peaks at 1435,2854 and 2924cm-1 in the SMZ spectrum.This data confirmed the loading of HDTMA onto the Zeolite surface.(Nezamzadeh-Ejhieh and Mirzaeyan,2011)
From X-ray diffraction study the composition was found to be C12 H8Cl4 O48Si24 in fig-3
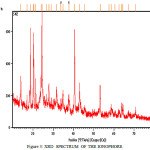 |
Figure 3: XRD SPECTRUM OF THE IONOPHORE Click here to View Figure |
Fabrication of Ion Selective Electrode
A copper wire was polished with emery paper &it was washed with distilled water and THF.The copper was dipped into the concentrated solution (0.3g of ionophore+0.1g of DOP+PVC+3 ml of THF) for some minutes,so that a non-transparent coating was formed.The wire was taken out from the mixture and dried overnight.The electrode was finally conditioned to attain stable equilibrium for 10 days by dipping in 1MCaCl2.The electrode was kept in distilled water when not in use.
Potential Measurements
All the membrane electrode potential measurements were performed at constant temperature (30°C) using digital potentiometer (EQUIP-TRONICS EQ 602) in configuration with silver electrode as a reference electrode. The representation of electrochemical cell for the EMF measurement is as follows.
| InternalReferenceElectrode(immobilisedCu wire) | InternalReference(1M CaCl2Solution) | ExternalReferenceElectrode(Ag/AgCl) |
Results and Discussion
Working Concentration Range and Slope of Ca2+ Sensor
Electrode Response
The electrode potential for a series of standard solution of Ca(II) ions was measured using potentiometer.The electrode gave a linear response to Ca(II) ion concentration range of 1M to 1×10-4M.The values are given in Table-1.Standard Electrode potential(E°) was determined by standard methods (Gurtu and Gurtu,2011) at 25°C,it was found to be 0.023V.The slope value was obtained from the calibration curve fig-4 and it was found to be 33 mv/decade.
table1
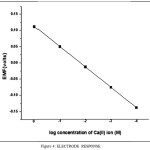 |
Figure 4: ELECTRODE RESPONSE Click here to View Figure |
Table 1: ELECTRODE RESPONSE
| Concentration of CaCl2 (M) | EMF(Half Cell Potential) volts |
| 1 | 0.135 |
| 1×10-1 | 0.044 |
| 1×10-2 | -0.033 |
| 1×10-3 | -0.083 |
| 1×10-4 | -0.116 |
| 1×10-5 | -0.116 |
Effect of PH on Electrode Response
The effect of pH on the response of electrode was studied in this work. The electrode potential of standard Ca(II) solution of varying pH had been measured. It was found that the electrode worked well over a pH range of 5.57to 6.24 .Table-2
Table 2: Effect of pH
|
Conc (M) of Ca2+ ion |
E.M.F (Half cell potential)Volts | PH 3.42 | PH 4.63 |
PH 5.57 |
PH 6.24 |
| 1 | 0.135 | -0.067 |
0.109 |
0.133 |
0.139 |
| 1×10-1 | 0.044 | -0.037 |
-0.006 |
0.041 |
0.048 |
| 1×10-2 | -0.033 |
-0.114 |
-0.094 |
-0.04 |
-0.028 |
| 1×10-3 | -0.083 |
-0.117 |
-0.096 |
-0.008 |
-0.080 |
| 1×10-4 | -0.116 |
-0.117 |
-0.101 |
-0.090 |
-0.080 |
Effect of Medium
The influence of the electrode was alsoninvestigated in a partially non-aqueous media using 25-75% water-acetone,water-DMA,&water-ehanol.The working non-aqueous media of the electrode was found to be 25%acetone medium, DMA medium in the conc of 10-4M Ca2+ ion.50% of ethanol medium in the concentration range of10-2M of Ca2+ ion.
Table-3
| Conc.Ca2+Solution(M) | E.M.F(Volts) | Acetone25% | Acetone50% | Acetone75% | Ethanol25% | Ethanol25% | Ethanol75% | DMA25% | DMA50% | DMA
75% |
| 1 | 0.135 | 0.129 | 0.146 | 0.195 | 0.013 | 0.136 | 0.140 | 0.137 | 0.145 | 0.164 |
| 1×10-1 | 0.044 | 0.038 | 0.022 | -0.103 | -0.036 | -0.042 | 0.051 | 0.050 | 0.067 | 0.0981 |
| 1×10-2 | -0.033 | -0.034 | -0.030 | -0.063 | -0.114 | -0.033 | -0.029 | -0.031 | -0.025 | -0.021 |
| 1×10-3 | -0.083 | -0.083 | -0.121 | -0.038 | -0.078 | -0.110 | -0.089 | -0.081 | -0.083 | -0.012 |
| 1×10-4 | -0.116 | -0.121 | -0.056 | -0.091 | -0.042 | -0.102 | -0.081 | -0.119 | -0.051 | 0.002 |
Selectivity
The potential response of the prospoed electrode to common cations were investigated by fixed interference method.(Semi-empirical Nicolski-Eisenmans equation).It was found that the potential remains unaffected in the presence of Na+&K+ cation.
Table 4
|
CATIONS |
SELECTIVITY CO-EFFICIENT VALUES |
|
Na+ |
3.2X10-5 |
| K+ |
6×10-5 |
Analytical Applications
The new prepared electrode was successfully used as an indicator electrode for EDTA titration with Ca2+ ions in the laboratory.(Fig-5)
 |
Figure 5: EDTA Titration With Calcium Click here to View Figure |
Conclusion
A new simple ,highly specific&selective calcium ion electrode has been prepared.The life time of the prepared electrode was found to be 5 months with good reproducibility of E.M.F values.
Reference
- Shamsipur.M , Soleymanpour.A , Akhond.M, Sharghi,.H and Massah,A.R“Uranyl selective PVC membrane electrodes based on some recently synthesized benzo-substituted macrocyclic diamides,” Talanta,2002,. 58, 2, 237–246,
CrossRef - ZhangZ.R and Yu,R.Q “The synthesis and membrane transport characteristics of macrocyclic polyether ligands composed of 1,10-phenanthroline as carriers for primary amine species,” Talanta, 1994 41, . 2, . 327–333, .
- Singh,A.K Saxena.P Mehtab.S and Gupta.B “Strontium(II)- selective electrode based on a macrocyclic tetraamide,” Talanta,2006 . 69, 2, . 521–526,
CrossRef - Singh,A.K Saxena,P and Panwar, A“Manganese(II)-selective PVC membrane electrode based on a pentaazamacrocyclic manganese complex,” Sensors and Actuators B,2005 .,110. 2,.377-381.
- Ganjali, M.R, Razavi,T , Dinarvand,R , Riahi,.Sand Norouzi.P “New diltiazem potentiometric membrane sensor stands on theoretical calculations as a useful device for diltiazem hydrochloride analysis in pharmaceutical formulation and urine,” International Journal of Electrochemical Science,2008,. 3,. 1543–1558,
- GanjaliM.R, Memari.Z Faridbod.F and Norouzi.P “Samarium microsensor: an asymetric potentiometric membrane sensor,” International Journal of Electrochemical Science, 2008,3,.1169-1179.
- Beheshti S.S,and AminiM.K, “A simple and selective flow injection potentiometric method for determination of iodide based on a coated glassy carbon electrode sensor,” International Journal of Electrochemical Science,2007. 2,. 778–787,
- Zhang.H , Zhang.Z, Li.J and Sh. Cai, “Effects of Mg2+ on supported bilayer lipid membrane on a glassy carbon electrode during membrane formation,” International Journal of Electrochemical Science,2007 .,2, 788–796,
- Paker.P, McGraw-Hill Concise Encyclopaedia of Science and Technology,1994 McGraw-Hill, New York, NY, USA,
- D’Souza,.S.F,“Microbial biosensors,” Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2001,. 16,. 6,. 337–353,
CrossRef

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.









